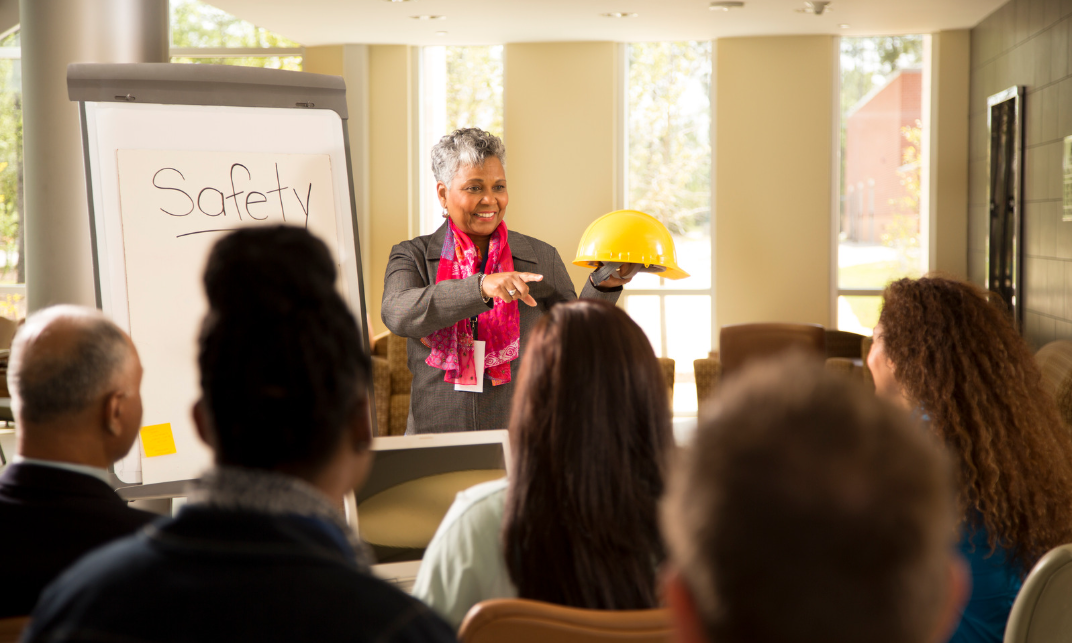
“The best way to predict the future is to create it.” – Abraham Lincoln. Safety Instructors are the creators of a safer future for employees in the workplace. These professionals play a critical role in promoting safety by educating and training employees on a variety of important safety topics. From hands-on demonstrations to interactive training sessions, Safety Instructors use innovative methods to engage and inform employees, ensuring they have the knowledge and skills necessary to work safely. With a growing emphasis on workplace safety, a career as a Safety Instructor offers a unique opportunity to make a difference and shape a safer future for all.
Safety Officer
A Safety Officer has a critical role in any organization and is responsible for ensuring the well-being of employees and visitors. In 1989, the Exxon Valdez oil spill in Alaska served as a vivid reminder of the importance of having a dedicated safety professional on board who can identify and mitigate potential hazards before they become a disaster. A Safety Officer can help prevent accidents and injuries, enforce safety policies and procedures, and promote a culture of safety within the workplace.

What is the Average Annual Salary of 'Safety Officer'?
$54,760

USA
£30,744

UK
Explore Career
Introduction
On average, one workplace fatality occurs every 99 minutes in the United States. This sobering statistic highlights the critical importance of workplace safety and the crucial role that Safety Officers play in protecting the lives of employees, visitors, and the public. These dedicated professionals work tirelessly to identify and mitigate potential hazards, enforce safety regulations, and provide training and education on a wide range of safety topics.
Also known as
- Health and Safety Officer
- Safety and Health Manager
- Safety Compliance Officer
- Safety Specialist
- Environmental Health and Safety Specialist
Typical Job Responsibilities
- Develop and implement safety policies and procedures
- Conduct safety inspections and assessments
- Investigate accidents and incidents to determine causes and prevent future occurrences
- Provide training and education on safety topics to employees and management
- Monitor and enforce compliance with safety regulations and standards
- Maintain accurate records of safety incidents and reporting requirements
- Conduct regular safety drills and emergency response exercises
Standard Work Environment
Safety Officers work in various settings, including manufacturing, construction, healthcare, and office buildings. The work environment can be fast-paced and high-stress, as Safety Officers are responsible for responding to emergency situations and managing potential hazards.
Work Schedule
Safety Officer positions may be full-time or part-time and may require on-call availability and the ability to respond to emergency situations outside of normal business hours. Some Safety Officers may be required to work shifts or weekends, depending on the needs of the employer.
Employers
- Manufacturing facilities
- Construction sites
- Healthcare facilities
- Office buildings
- Retail stores
- Government agencies
- Universities and colleges
- Transportation companies
Unions / Professional Organizations
Safety Officers may belong to professional organizations, such as the National Safety Council or the American Society of Safety Professionals, to stay current on industry trends and best practices. They may also be members of labor unions, such as the International Association of Fire Fighters, to negotiate their employment contracts and benefits.
Workplace Challenges
- Keeping up with changes in safety regulations and standards
- Balancing the need for safety with productivity and efficiency goals
- Responding to emergency situations and managing potential hazards
- Maintaining employee compliance with safety policies and procedures
- Managing conflicting priorities and competing demands
Projected Career Map
Safety Officers typically begin their careers in entry-level positions and can advance to supervisory or management positions with experience and education. Advancement opportunities may include roles such as Safety Manager, Director of Environmental Health and Safety, or Corporate Safety Director.
Job prospects
The demand for skilled Safety Officers continues to grow, particularly in industries such as construction, manufacturing, and healthcare. Job prospects are favorable for individuals with a strong background in safety regulations and best practices, as well as experience in various settings.
Beneficial Professional Development
Continuing education and professional development are critical for Safety Officers to stay current on industry trends and best practices. Earning certifications and participating in workshops can enhance a safety officer’s credibility and demonstrate their expertise in the field. Pursuing specialization in a particular area of safety, such as hazardous materials management or industrial hygiene, can deepen a safety officer’s knowledge and expertise in their field.
By pursuing these professional development opportunities, safety officers can enhance their knowledge and skills, keep up with regulatory changes, and effectively manage workplace risks. This can lead to safer work environments, improved employee morale, and increased productivity.
Conclusion
Safety Officers play a vital role in promoting and ensuring the safety of employees and the public in the workplace. With the increasing emphasis on workplace safety, the demand for skilled Safety Officers continues to grow, offering favorable job prospects and opportunities for advancement. Pursuing ongoing education and professional development is critical for success in this field.
Advice from the Wise
You don’t need to know the whole alphabet of Safety. The A, B, C of it will save you if you follow it: Always Be Careful.
Holland Codes, people in this career generally possess the following traits
Realistic
Investigative
Artistic
Social
Enterprising
Conventional
United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals that this career profile addresses




































 ">
">