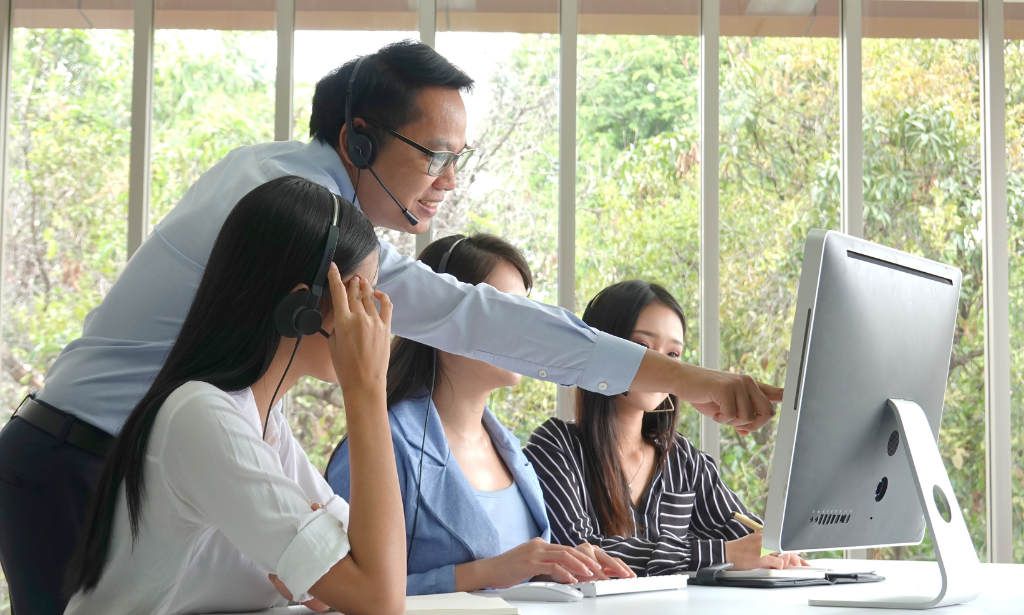
Team leadership is a crucial component of organizational success. A study by the Harvard Business Review found that effective team leaders possess an average of four unique skills: strategic orientation, team orientation, relationship orientation, and personal orientation. By balancing these skills, team leaders are able to drive their teams towards success, increase employee engagement and job satisfaction, and create a positive and productive work environment.
Operations Manager
Operations managers are the unsung heroes of organizations, working tirelessly to keep everything running smoothly. They are responsible for overseeing production processes, managing resources, and ensuring that quality standards are met. Without effective operations management, organizations would struggle to meet customer needs and achieve their goals.

What is the Average Annual Salary of 'Operations Manager'?
$72,209

USA
£48,512

UK
Explore Career
Introduction
Operations management is a vital aspect of any organization, and the operations manager is the individual responsible for overseeing the day-to-day running of business operations. From supply chain management to quality control, operations managers play a critical role in ensuring the success of their organizations.
Also Known as
- Production Manager
- Operations Director
- Supply Chain Manager
- Operations Coordinator
- Operations Supervisor
Typical Job Responsibilities
An Operations Manager is expected to –
- Oversee production processes and systems
- Manage resources, including personnel and equipment
- Ensure that quality standards are met
- Develop and implement policies and procedures
- Monitor and analyze performance metrics
- Identify areas for improvement and implement changes
- Manage budgets and control costs
- Collaborate with cross-functional teams, including sales, marketing, and product development
- Analyze market trends and customer demand to optimize production and supply chain processes
- Ensure compliance with regulations and industry standards
- Negotiate contracts and manage relationships with suppliers and vendors
- Lead and motivate a team of supervisors and coordinators to achieve goals and objectives
- Respond to customer inquiries and resolve operational issues as needed.
Standard Work Environment
Operations managers typically work in an office setting, although they may also spend time in production facilities or warehouses. They work with a wide range of individuals, including employees, vendors, and customers, and must be able to communicate effectively with all stakeholders.
Work Schedule
Operations managers typically work full-time and may be required to work overtime or be on call to resolve operational issues. The nature of their work may also require travel to other locations or attendance at off-site meetings.
Employers
An Operations Manager can expect to find jobs in the following –
- Manufacturing Companies
- Retailers
- Service Providers
- Healthcare Organizations
- Government Agencies
Unions / Professional Organizations
Operations managers may be members of professional organizations, such as the Institute of Operations Management or the Association for Supply Chain Management. These organizations offer training and development opportunities, as well as networking and career advancement opportunities.
Workplace Challenges
- Managing personnel and resources effectively
- Staying up-to-date with industry developments and trends
- Adapting to changes in technology and automation
- Balancing competing priorities and conflicting demands
- Maintaining positive relationships with employees, vendors, and customers
Projected Career Map
Operations managers typically begin their careers as supervisors or coordinators and may advance to senior management positions, such as director of operations or chief operating officer. Some operations managers may also choose to specialize in a specific area, such as supply chain management or quality control.
Job Prospects
The demand for operations managers is expected to grow in line with the overall growth of the economy. In particular, the healthcare and retail sectors are projected to experience significant growth and will provide a wealth of job opportunities for operations managers.
Beneficial Professional Development
Continuous learning and professional development are important for operations managers, as they must be able to stay up-to-date with industry trends and developments. This may include attending conferences and workshops, earning certifications, and taking courses in areas such as supply chain management, project management, and data analysis.
Conclusion
Operations managers play a vital role in the success of any organization, and their work is critical to ensuring the smooth operation of daily activities. With the proper training and experience, operations managers can enjoy a rewarding and challenging career with opportunities for growth and advancement. Whether you’re just starting out or looking to advance your career, a career in operations management is well worth considering.
Advice from the Wise
Perfection is not attainable, but if we chase perfection we can catch excellence.
Holland Codes, people in this career generally possess the following traits
Realistic
Investigative
Artistic
Social
Enterprising
Conventional
United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals that this career profile addresses




































 ">
">